 |
|
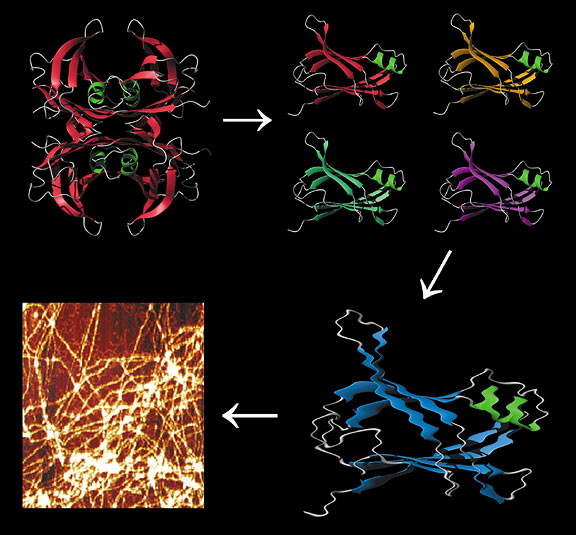
| The figure depicts the pathway by which transthyretin misfolding leads to amyloid fibrils (shown in the bottom left panel). Rate limiting tetramer dissociation followed by a conformational change in the normally folded monomer forms the misassembly competent amyloidogenic intermediate leading to fibrils. |