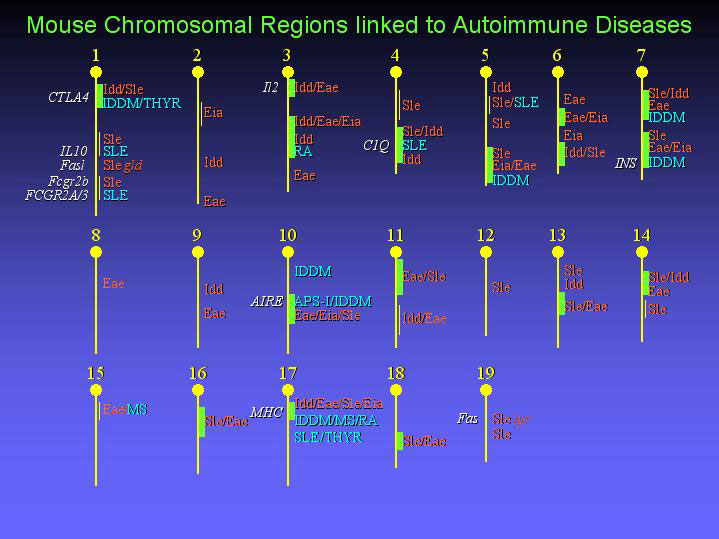
Key:
White
CTLA4 -- encodes an inhibitory T cell molecule
IL10 -- interleukin 10 gene
IL2 -- interleukin 2 gene
Fasl -- the gene encoding the ligand for the fas gene product
Fas -- fas gene
INS -- insulin gene
AIRE -- autoimmune regulator gene
C1Q -- encodes a protein that activates the complement cascade
MHC -- major histocompatability complex gene
Fcgr2b -- Fc gamma receptor 2b gene
FCGR2A/3 -- Fc gamma receptor 2a gene
Blue
APS-I -- autoimmune polyglandular syndrome
IDDM -- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
MS -- multiple sclerosis
SLE -- systemic lupus erythematosus
THYR -- thyroiditis
RA -- rheumatoid arthritis
Red
Idd -- insulin-dependent diabetes
Eia -- experimentally induced arthritis
Eae -- experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Sle -- systemic lupus erythematosus
gld -- generalized lymphoproliferative disease (FasL mutation with lupus)
lpr -- lymphoproliferation gene (Fas mutation with lupus)