Reversed Rotation of Myosin VI
 |
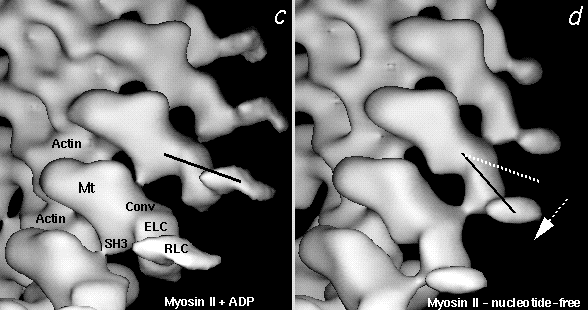 |
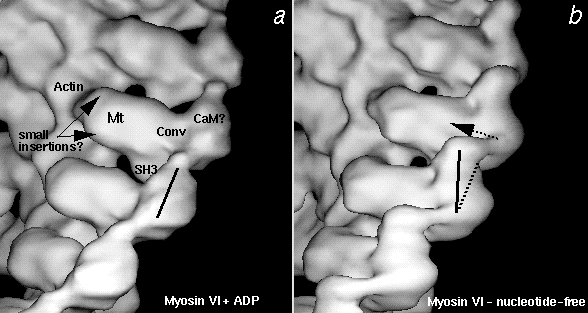
Figure 4. Comparison of the ADP (left) and nucleotide-free (right) 3D maps of myosin VI (a,b) and smooth muscle myosin II (c,d) attached to F-actin. All maps are at the same scale, the vertical extent of the maps in a & b is ~250 Å. Solid lines indicate the long axes of the calmodulin or light chain binding domains of the 2 myosins. Arrows show the direction of rotation of the domains when ADP is released. The rotation was roughly 10-20° for myosin VI and 23° for myosin II. Beta denotes the N-terminal SH3 domain, Mt is the catalytic core of myosin. 'Small insertions?' highlights possible locations of 9 and 13 amino acid insertions in the myosin VI sequence. 'Conv' denotes the approximate location of the converter regions. 'CaM?' is the probable location of the calmodulin light chain in myosin VI. ELC and RLC are the essential light chain and the regulatory light chain, respectively, which, together with a long heavy chain helix, constitute the lever arm of myosin II (see Wells et al., 1999)
Return to the Actomyosin Cryo-Electron Microscopy
contents © 2000
awl



